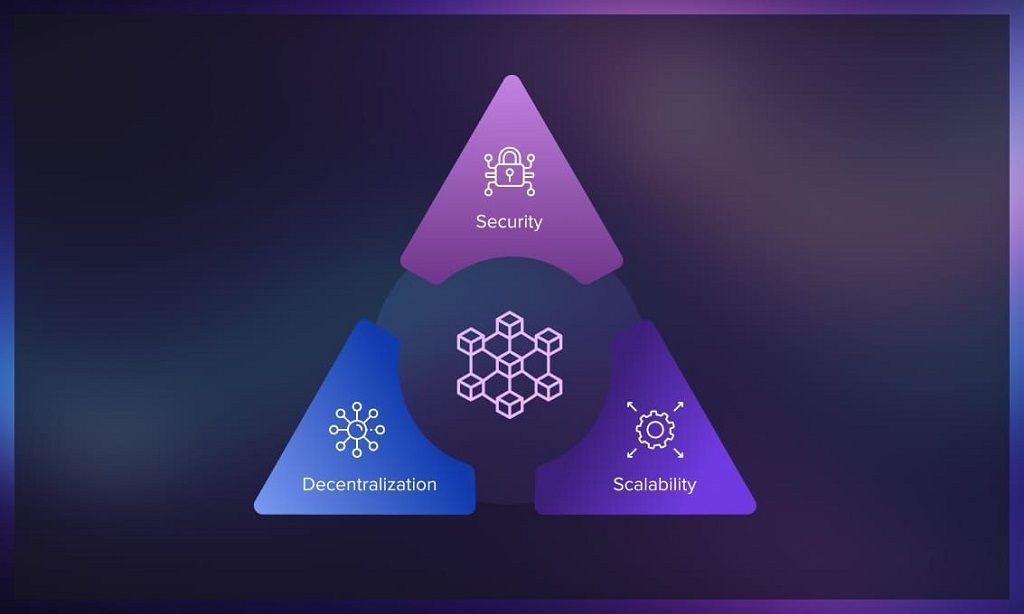
Decentralized Network Scalability Challenges and Solutions
As we look to the future of technology, decentralized networks are at the forefront of innovation. These systems, powered by blockchain technology, are promising to revolutionize industries by eliminating intermediaries, increasing transparency, and offering unprecedented levels of security. However, as these networks grow in popularity, they face one key issue—scalability. To explore future solutions, consider looking at platforms like the Future Life Network, which provides insights into overcoming these challenges.
Understanding the Scalability Problem in Decentralized Networks
In decentralized systems, every node operates autonomously, without a central authority overseeing operations. While this structure provides numerous benefits such as security, privacy, and redundancy, it also introduces a scalability problem. As these networks grow and more users join, the overall load increases exponentially, leading to slower transaction speeds, higher latency, and increased costs for processing data.
A recent study from the Blockchain Research Institute reveals that the Ethereum blockchain, for example, processes just around 30 transactions per second (TPS). This is significantly lower compared to centralized payment processors like Visa, which handles up to 65,000 TPS. As decentralized networks scale, these limitations become more apparent, creating friction in widespread adoption.
The scalability issue primarily arises from how decentralized networks function. When a network grows, so does the amount of data that needs to be processed and stored. In traditional systems, scaling can be achieved by adding more servers or increasing bandwidth. However, in a decentralized environment, every additional node must synchronize with the entire network, creating potential bottlenecks that can hinder performance.
Nodes in a Decentralized Network: The Unsung Heroes
One of the key components of decentralized networks are the Nodes in a Decentralized Network. These nodes, which are independent devices or computers within the network, are responsible for validating transactions and maintaining the integrity of the blockchain. The more nodes in the network, the more secure it becomes, but also the more complex the process of maintaining scalability.
As decentralization grows, the responsibility of each node expands. The synchronization of thousands, if not millions, of nodes is crucial for network consensus, and this distributed nature introduces significant delays in transaction verification. In other words, as the number of nodes increases, the time it takes to reach consensus grows exponentially.
Moreover, nodes in a decentralized network often need to store vast amounts of data. This data must be replicated across the network to ensure security, which leads to increased storage requirements for all participants. This means that scaling the network in terms of both performance and data storage requires solutions that can handle the increasing number of nodes, as well as the need for faster transaction speeds and lower latency.
Innovative Solutions to Decentralized Network Scalability
Fortunately, several solutions are emerging to address scalability challenges in decentralized networks. These innovations focus on optimizing data handling, improving consensus mechanisms, and utilizing advanced technologies like sharding and off-chain solutions.
Sharding: The Future of Scalability
One of the most promising approaches to improving scalability in decentralized networks is sharding. This technique involves breaking the blockchain into smaller, more manageable pieces, or “shards,” that can process transactions in parallel rather than sequentially. Each shard processes a subset of the overall data, allowing for faster transaction speeds and improved scalability.
Sharding has been implemented in various blockchain platforms, including Ethereum 2.0, where it aims to increase the network’s transaction throughput by over 100x. With sharding, decentralized systems can handle a much larger number of transactions without overwhelming the network or compromising on decentralization.
Layer 2 Solutions: Scaling Without Compromising Decentralization
Another solution gaining traction is Layer 2 scaling solutions. Layer 2 refers to protocols built on top of a blockchain network to improve its scalability and efficiency without altering the underlying blockchain protocol. Popular Layer 2 solutions include Lightning Network for Bitcoin and Optimistic Rollups for Ethereum.
These solutions allow transactions to be processed off-chain, reducing the burden on the main blockchain while still benefiting from its security features. By offloading transactions to secondary layers, these protocols can handle thousands of transactions per second, significantly increasing the scalability of decentralized networks.
Read More Also: Steampunk Style In The Interior Of The Apartment
Consensus Mechanisms: From Proof-of-Work to Proof-of-Stake
The consensus mechanism used in decentralized networks is another area ripe for innovation. In traditional blockchain systems like Bitcoin, the Proof-of-Work (PoW) mechanism is used to verify transactions. However, PoW is energy-intensive and can be slow, especially as the network grows.
Proof-of-Stake (PoS) is an alternative consensus mechanism that is gaining popularity due to its lower energy consumption and faster transaction processing capabilities. Ethereum, for example, has transitioned to PoS with Ethereum 2.0, aiming to reduce its environmental impact and improve scalability. PoS allows for faster block times and more efficient transaction validation, enabling decentralized networks to scale more effectively.
Off-Chain Data Storage and Processing
Another approach to scaling decentralized networks is off-chain data storage and processing. By moving data off the blockchain and onto external servers, decentralized systems can reduce the load on the main chain, speeding up transaction times and reducing costs. For example, technologies like InterPlanetary File System (IPFS) allow data to be stored in a decentralized manner off-chain while still maintaining the security and integrity of the system.
Off-chain processing can also improve scalability by enabling faster data retrieval and reducing the need for every node to store and verify every transaction. This can significantly increase the throughput of decentralized networks, allowing them to handle a much larger volume of transactions.
The Road Ahead: Decentralized Networks in the Future
Looking forward, decentralized networks are poised to become a cornerstone of our digital future. With innovations like sharding, Layer 2 solutions, PoS, and off-chain processing, the scalability issues that once seemed insurmountable are being tackled head-on.
By adopting these strategies, decentralized networks can become more efficient, cost-effective, and user-friendly, ensuring that they are ready for widespread adoption in industries ranging from finance to healthcare to supply chain management. The scalability challenges may still be complex, but with continued research, development, and innovation, the future of decentralized networks is brighter than ever.
Summary
Decentralized network scalability remains a pressing issue, but innovative solutions are emerging to address these challenges. Sharding, Layer 2 solutions, PoS, and off-chain processing are some of the most promising technologies that could pave the way for scalable and efficient decentralized systems. As these advancements continue to evolve, decentralized networks will become more viable for mainstream adoption, transforming industries and paving the way for a more decentralized future.