Thermal Bridging Solutions for Energy Efficiency
Improving energy efficiency in buildings starts with tackling thermal bridging. These hidden heat transfer pathways can undermine insulation, elevate energy costs, and reduce comfort. By addressing this issue with innovative solutions, you can dramatically improve building performance while supporting sustainability. From construction materials to installation techniques, the options are endless. Ready to transform your energy efficiency game? Let’s dive in. Don’t forget to explore Bestusatools for essential tools and resources to enhance your projects.
Understanding Thermal Bridging and Its Impact
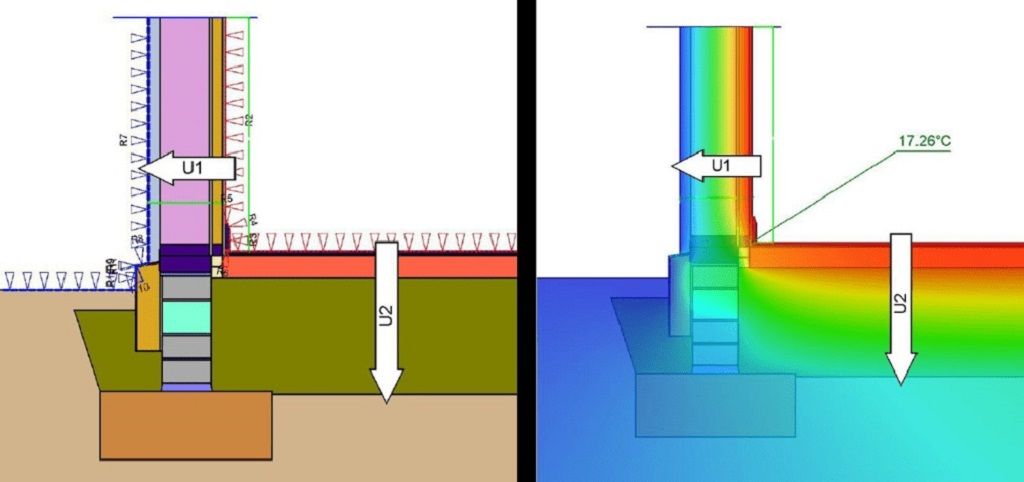
Thermal bridging occurs when heat flows through a material that is more conductive than the surrounding insulation. Common culprits include steel beams, concrete, and poorly insulated windows. This phenomenon accounts for up to 30% of energy loss in some buildings, according to the U.S. Department of Energy.
Read More Also: Key Steps to Start Your E-commerce Company
Key Impacts of Thermal Bridging:
- Increased Energy Costs: Compromised insulation forces HVAC systems to work harder.
- Comfort Issues: Uneven temperatures can lead to cold spots or drafts.
- Condensation Risks: Thermal bridges can result in moisture buildup, causing mold or structural damage.
- Environmental Concerns: Excess energy consumption contributes to greenhouse gas emissions.
By understanding these impacts, property owners and builders can prioritize effective thermal bridging solutions for energy efficiency.
How to Identify Thermal Bridging in Buildings
Thermal imaging cameras are invaluable for detecting these weak points. By revealing temperature differentials in walls, roofs, and floors, you can quickly pinpoint areas needing attention. Key areas to inspect include window frames, floor junctions, and wall-to-roof connections. A professional energy audit often identifies thermal bridging more comprehensively.
Material Choices for Thermal Bridging Reduction
The materials used in construction play a pivotal role in minimizing thermal bridging. Selecting low-conductivity options helps to disrupt heat flow pathways.
Innovative Materials Include:
- Aerogels: Ultra-light and highly insulating.
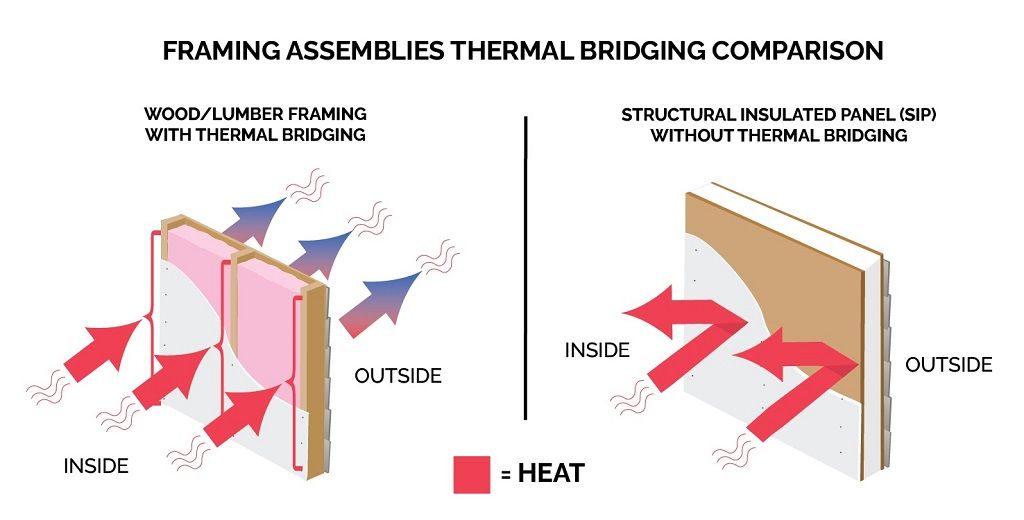
- Structural Insulated Panels (SIPs): Combine insulation with robust structural support.
- Thermal Breaks: Materials like rigid foam placed between conductive elements to block heat transfer.
While the upfront cost of these materials may be higher, they offer long-term savings by enhancing energy efficiency and reducing utility bills.
Effective Design Strategies to Combat Thermal Bridging
Smart building designs integrate thermal bridging solutions from the outset. Incorporating proper planning into the construction phase can significantly reduce remediation costs later.
Key Strategies:
- Continuous Insulation: Ensures uninterrupted thermal protection across all building surfaces.
- Offset Stud Walls: Limits direct contact between exterior and interior walls.
- Improved Window Placement: Strategically position windows to minimize exposure to conductive materials.
Additionally, when selecting construction tools, it’s essential to choose the right nail gun for precision and durability.
Best Practices for Retrofitting Existing Buildings
Existing structures often suffer from substantial heat loss due to outdated designs. However, retrofitting with thermal bridging solutions can mitigate this issue effectively.
Retrofitting Techniques:
- Exterior Cladding Insulation: Adds a continuous insulating layer over external walls.
- Sealants and Tapes: Eliminate gaps in insulation or around windows.
- High-Performance Glazing: Replace standard windows with energy-efficient alternatives.
Studies reveal that retrofitting insulation can reduce annual energy costs by 20-50%, depending on climate and building type.
Thermal Bridging and Building Codes
Modern building codes increasingly emphasize thermal performance. Standards like LEED, BREEAM, and Passive House certifications require stringent insulation practices. Compliance ensures not only energy savings but also market value enhancements for the property.
The Role of Technology in Thermal Bridging Solutions
Advanced technologies are transforming the construction industry. Tools like Building Information Modeling (BIM) allow architects to simulate and analyze thermal performance before construction begins. Similarly, heat-resistant coatings and self-healing materials offer futuristic options for thermal bridging reduction.
Case Studies: Successful Thermal Bridging Mitigation
- Commercial Buildings: A Seattle office complex cut energy costs by 40% using aerogel panels.
- Residential Properties: A Canadian housing project achieved Passive House standards by employing continuous exterior insulation.
These examples illustrate how strategic solutions lead to tangible results.
FAQs
What is thermal bridging?
Thermal bridging refers to heat transfer through conductive materials in a building, often reducing overall insulation performance.
Why is reducing thermal bridging important?
Reducing thermal bridging enhances energy efficiency, cuts utility costs, and promotes sustainability.
What are common thermal bridging solutions?
Solutions include continuous insulation, thermal breaks, advanced materials, and high-performance glazing.
Can thermal bridging be fixed in older homes?
Yes, retrofitting techniques like cladding, sealants, and improved windows can address thermal bridging in older buildings.
What is the cost of implementing thermal bridging solutions?
Costs vary based on the technique and materials but are generally offset by long-term energy savings.
How does thermal bridging impact the environment?
By increasing energy usage, thermal bridging contributes to higher greenhouse gas emissions.
Conclusion
Thermal bridging is a critical challenge in achieving energy-efficient buildings. By adopting innovative materials, smart design strategies, and advanced technologies, you can mitigate its effects and enjoy lasting energy savings.